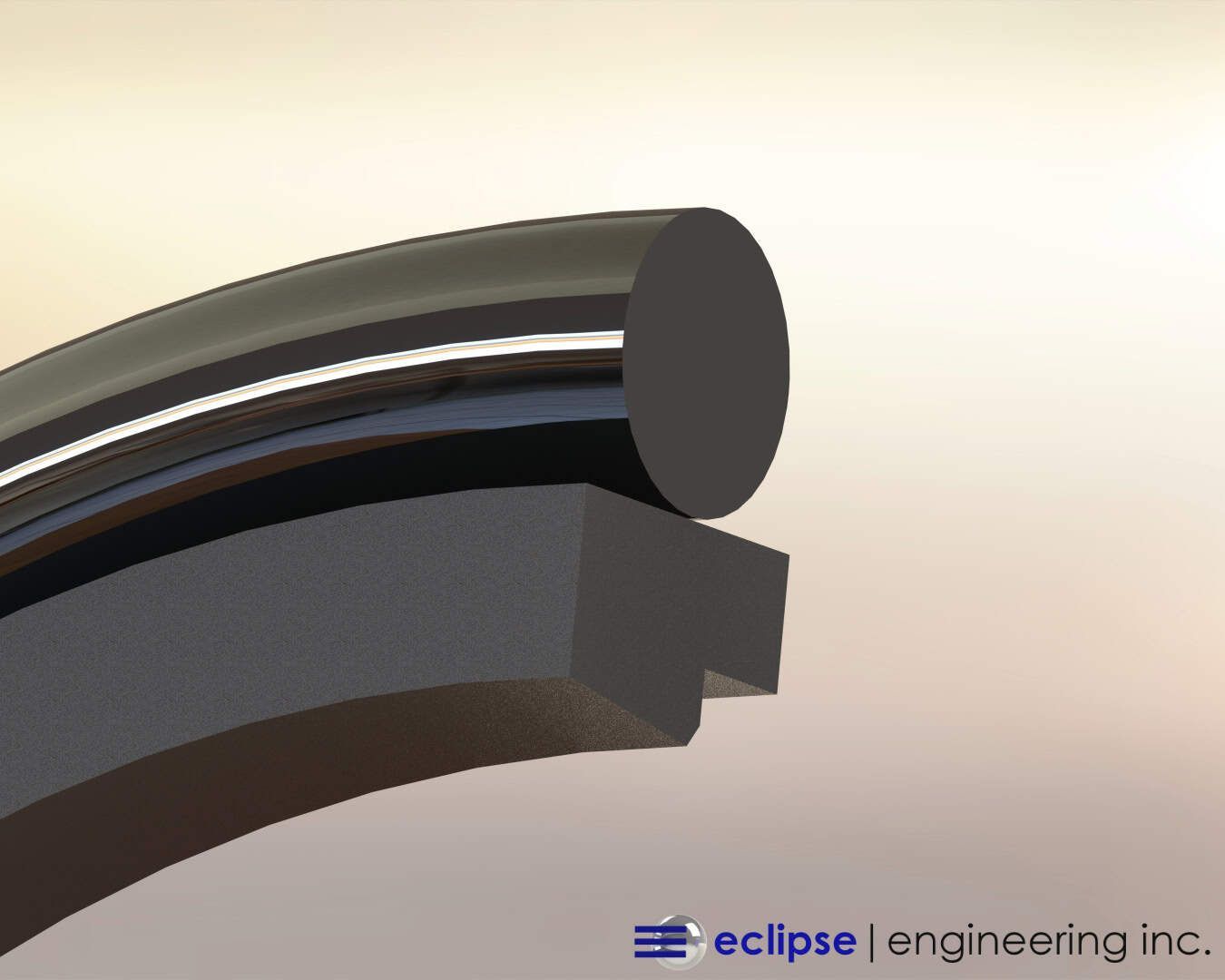
The Advantages and Disadvantages of PTFE O-Rings

While most common O-Ring materials are rubber or elastomeric compounds, certain operating conditions and hardware configurations merit the use of PTFE as the material.
PTFE offers many distinct advantages over elastomers. These advantages include corrosion resistance, massive temperature range capabilities, excellent electrical properties and an almost unlimited shelf life, to name a few.
But some considerations should be taken into account before making the switch to a PTFE O-Ring.
1966 Mr. America & Sports Performance Pioneer Bob Gajda Discusses Bodybuilding Experiences (Part 1)! buy anavar bpi bulk muscle gainer review, crazy bulk reviews bodybuilding | profile While PTFE offers some distinct advantages over elastomers, it also has some draw-backs that can negatively affect seal performance.
Eclipse offers fully customized PTFE O-Ring sizes out of our full range of PTFE blends that can help boost performance and longevity for your seals. But in some cases, an Eclipse Spring Energized seal might be the best choice for optimal sealing performance.
Here’s how to determine whether a PTFE O-Ring or Spring Energized seal is the best for your application.
Advantages of PTFE O-Rings
Chemical compatibly is often one of the first things checked when specifying an O-Ring material.
Corrosion resistance
Media that isn’t compatible with typical rubber compounds, or caustic or corrosive chemicals can make PTFE the best choice of material.
PTFE is impervious to almost all industrial chemicals, making it one of the most corrosion resistant materials available throughout all industries. And it the integrity of rubber compounds is being compromised by chemical attack, then PTFE may do the trick.
Long shelf-life
Applications requiring long-life or extended service intervals in corrosive environments may also merit the use of PTFE.
While some elastomers might survive for the short term or in intermittent exposure, degradation over time might result in problems years down the road, whereas PTFE’s resistance properties will remain indefinitely.
Wide temperature range capabilities
PTFE’s temperature range capability of -325°F to +500°F is also well beyond the range of most elastomers.
Applications in cryogenics or high temperature situations such as ovens or combustion processes may also rule out any elastomer compound, again making PTFE the best choice.
Extremely low temperatures will cause most rubber compounds to harden to the point where any elastomeric properties are no longer present in the material. This combined with contraction of the material can mean it will no longer function effectively as a seal.
PTFE, on the other hand, retains flexural and pliability properties even at cryogenic temperatures.
Additional Benefits to PTFE O-Rings
PTFE has some additional advantages over rubber compounds as well:
- Unlimited Shelf Life: PTFE doesn’t degrade with age and is unaffected by UV light, so age control is not typically necessary
- PTFE does not swell due to moisture absorption
- PTFE is not susceptible to explosive decompression
- Virgin PTFE is FDA Compliant
- PTFE has excellent electrical properties such as dielectric strength and electrical resistance
The Disadvantages of PTFE O-Rings
While chemical attack or extreme temperature might not leave any choice besides PTFE, there are some disadvantages to the material that could affect your project.
Higher hardness
Virgin PTFE’s hardness is 55 Shore D, which is much harder than a typical Nitrile O-Ring at 70 Shore A, which is a softer scale.
The higher hardness negatively affects sealability, as the material doesn’t conform the mating hardware surfaces as easily.
Leakage rate
While rubber O-Rings might conform to “as machined” surfaces, PTFE may require post-process surface finish improvements to control leakage to acceptable levels.
In general, under normal conditions, the leakage rate for a PTFE O-Ring will be higher than any elastomeric compound.
The use of a PTFE O-Ring isn’t recommended for applications that don’t require extreme temperature or severe chemical conditions.
Inelasticity
PTFE’s nature as an inelastic material means that reuse or multiple installations of the same seal will not be possible.
Unlike rubber compounds, PTFE will not return to it’s original shape and cross-section once deformed during installation and use. That means PTFE O-Rings are typically only recommended for static face seal or flange type configurations that are not actively engaged and disengaged.
For example, a PTFE O-Ring would not be recommended for a chamber door seal that needs to be opened and closed frequently, as the O-Ring would likely have to be replaced after every use.
A reused PTFE O-Ring may look and perform similarly to a standard rubber O-Ring suffering from extreme compression set. But unlike rubber, this compression set occurs after only one use.
More often, PTFE O-Rings are found in flange gasket type applications where the seal will remain static and undisturbed until the next service interval.
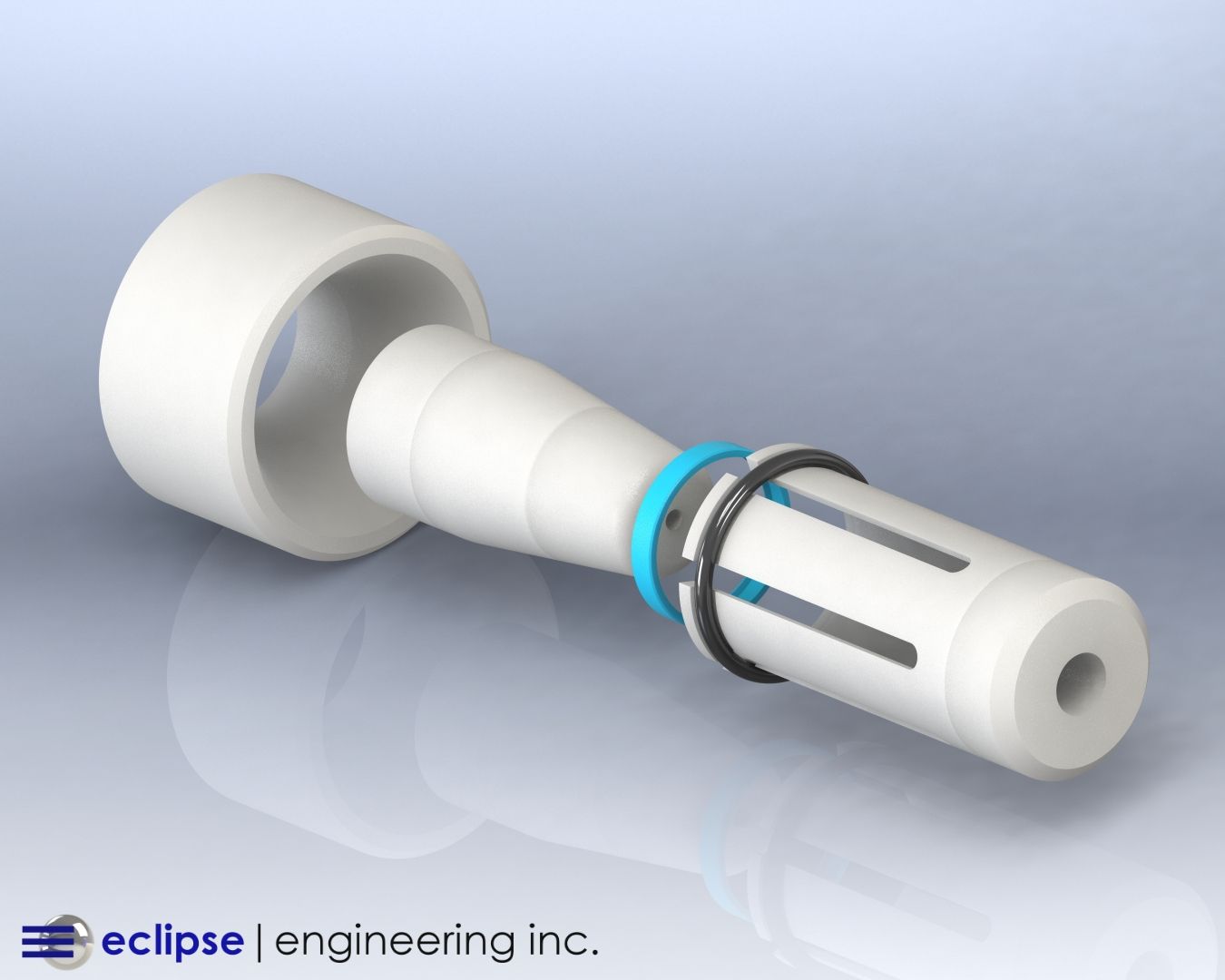
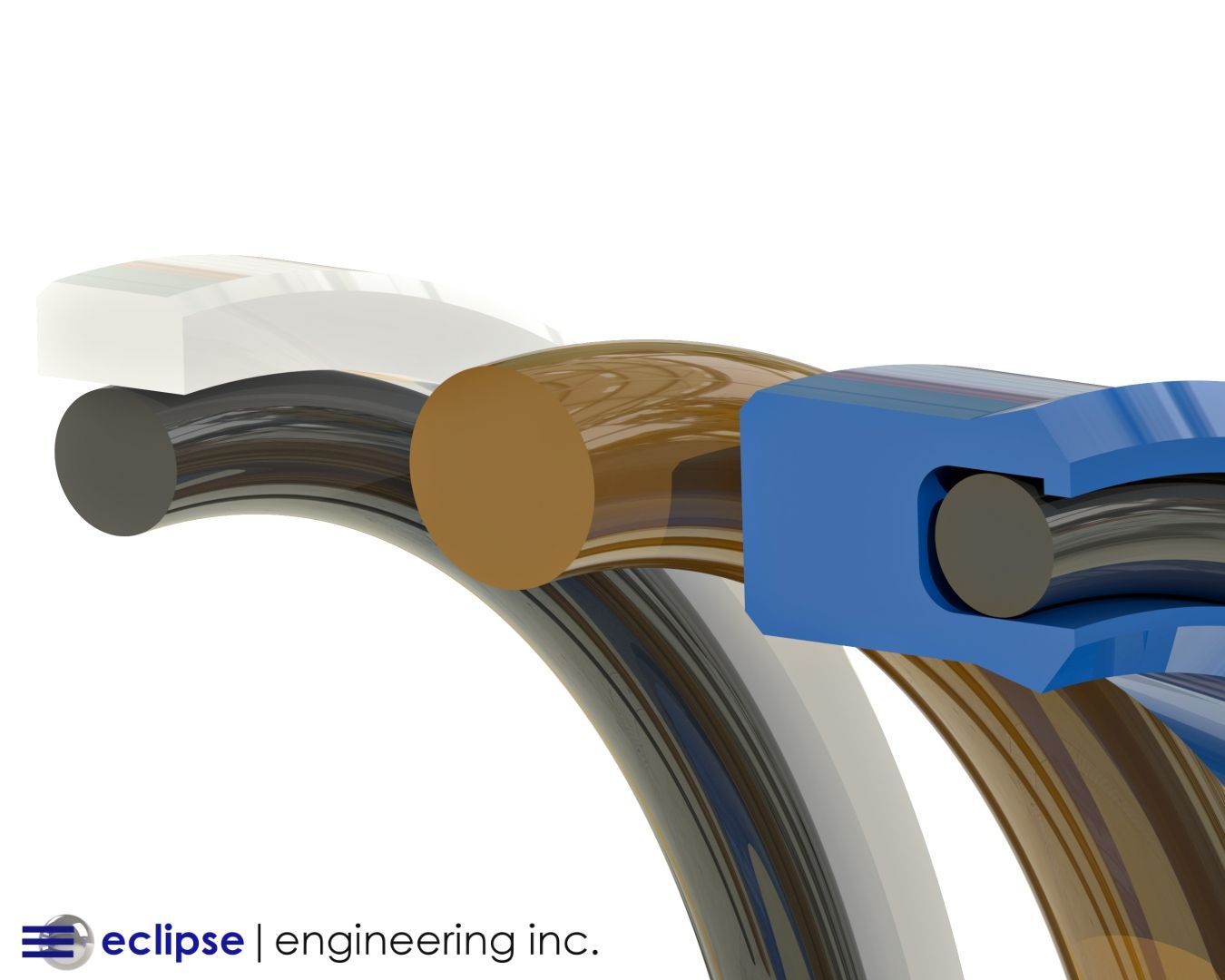
When to Choose an Eclipse Spring Energized Seal
When deciding whether to use a PTFE O-Ring for your application, the benefits of a spring energized seal should also be taken into consideration.
A spring-energized seal will retain all the benefits of using PTFE as a sealing material, but won’t be subject to the disadvantages PTFE has on its own.
Incorporation of a metallic spring within a seal jacket will allow the PTFE to be energized at all times.
The inelasticity and cold flow tendencies of PTFE no longer become a problem with the spring of a spring energized seal, which ensures the good contact of the sealing surfaces under all conditions. This allows high cycle rates and repeated installations to be possible with a spring energized seal.
Spring energized seals also provide improved sealabilty and friction performance compared to a PTFE O-Ring.
In applications where PTFE O-Rings need to be replaced often, a spring energized seal may be a better choice.
Custom PTFE O-Ring Sizes and Materials from Eclipse
PTFE O-Rings are prevalent in the seal market and can often be sourced off-the-shelf. But selection is usually limited to Virgin PTFE, as the material and sizes to AS568B standard dash numbers.
Eclipse’s in-house machining capabilities and expertise means custom O-Ring cross-sections and diameters can be made-to-order, without tooling cost.
Correct Sizing
Eclipse is often approached by customers who are rebuilding old equipment, or machinery sourced from over-seas that may not use standard O-Ring sizes.
When using PTFE, the correct size for an O-Ring becomes more critical since it won’t stretch or conform as easily as a rubber compound would.
In a situation where a standard dash size is in-between two diameters, it’s usually possible to stretch the smaller size elastomer O-Ring into a groove. Though this might not be possible with a PTFE O-Ring, so a custom machined size may be necessary in this instance.
Made-to-order machining also allows custom size cross-sections to adjust the squeeze or compression of the O-Ring.
High or low pressure customization
In high-pressure situations where high clamping force can be provided, a thicker than standard cross-section may improve sealing performance by increasing the squeeze and therefore contact area and force.
On the other side, an application where clamping loads are light or friction is a concern, a smaller than normal O-Ring cross-section could help meet application requirements or allow for proper assembly of the hardware.
Wide variety of PTFE blends
Custom machining by Eclipse also allows customers to choose O-Ring materials from Eclipse’s full line of PTFE blends and Polymer seal materials.
The addition of fillers to Virgin PTFE can greatly improve the mechanical properties, stability, and wear resistance. Glass-fibers or Graphite fillers can enhance mechanical properties and wear life significantly.
In applications where high pressure extrusion is an issue, a filled PTFE can drastically enhance performance and extend seal longevity.
Other fillers, such as the solid lubricant Molybdenum Disulfide, can considerably reduce friction in dynamic applications.
The presence of an internal lubricant will reduce interface surface temperatures, which is beneficial to enhancing durability and prolonging seal life.
Eclipse’s non-PTFE based polymers such as UHMW and Thermoplastic Elastomer are also readily available if the unique properties of those materials is better suited for the application.
Spring or O-ring energizers can extend the normal limits of PTFE and plastic materials to deliver durable ultra-tight sealing capability. Discover how energizers work and how they can elevate your next sealing challenge >