Designing Seals for Extreme Temperature Limits

The temperature limits of a seal can make or break the functionality of important machinery. And there’s maybe no example of this more palpable than the disastrous explosion of the Challenger, just 73 seconds into its flight.
The initial cause of failure was a Fluorocarbon O-ring that could not accommodate the cold temperature swing, along with the expansion of the O-ring joint. This combination allowed hot air gases to escape, burning a hole in the Hydrogen/Oxygen tank affixed to shuttle.
Although there are many factors behind the disaster, the temperature limit of the O-ring in the shuttle played a major role.
The Role of Temperature Limits in Seal Design
When we design product for sealing applications, there are a key few elements that drive the final design of the product: pressure, geometry of hardware, fluid compatibility, economics and, of course, temperature.
In benign environments, between 32 °F to 180 °F, most materials including rubber will normally survive and work well within the operating parameters.
But with many sealing applications, we see high temperatures over 400 and as high as 750 °F, or going in the opposite direction liquid oxygen sits around -300 °F. And if you wanted to make the molecules stop moving, you’ll need to get to near absolute zero or around -465 °F.
These extremes cause the designers at Eclipse to select the right materials for sealing, along with seal cross sections that will withstand these extremes.
When designing seals, we look at all the properties that affect seal ability.
Focusing on temperature often dictates the types of materials we’ll use. For example, we’ll use PCTFE to operate at -460°F or a Polyimide for temperatures in excess of 600°F.
If the range is narrow enough, we can utilize elastomers like specially compounded Nitriles which can go from -65 to 275 F. But we must develop sealing systems that accommodate these temperature spreads.
Sealing Systems to Accommodate Extreme Temperatures
We often turn to spring energized seals to cover the gaps, especially when our range exceeds what elastomers can handle.
This allows us to be mindful of the types of springs and the alloys we use to allow the spring to give us the physical properties necessary to accomplish sealing.
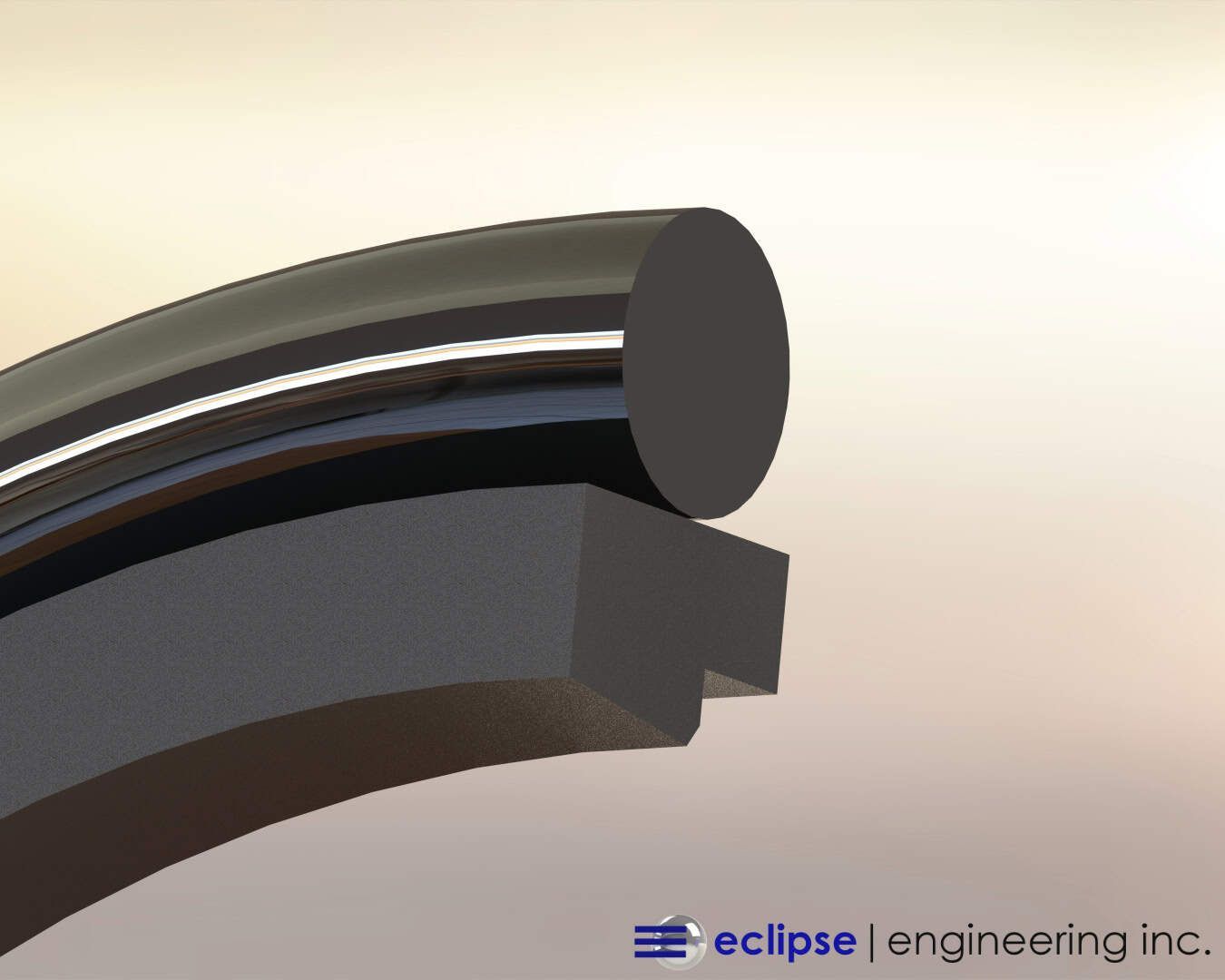
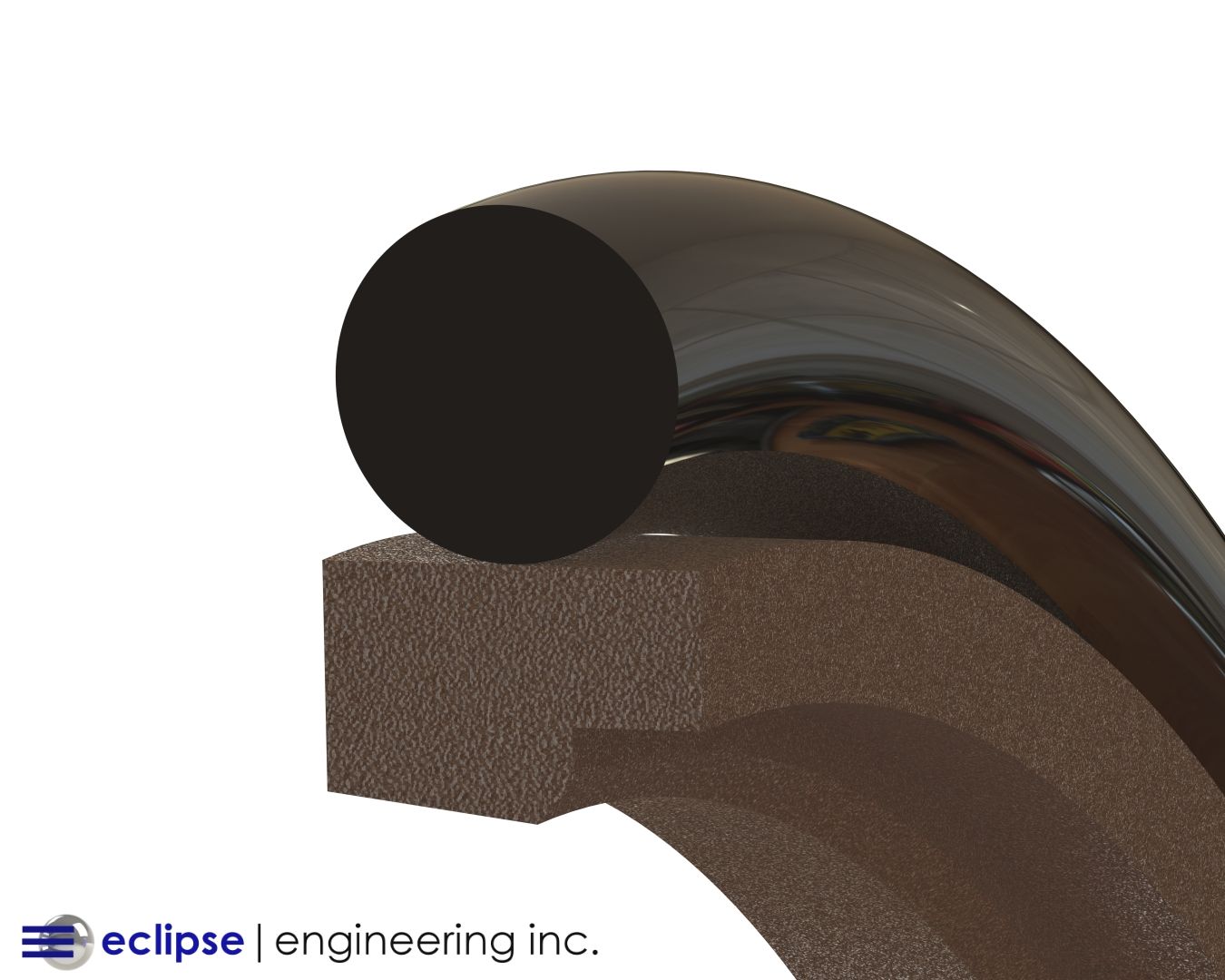
The use of back-up ring systems in conjunction with seals — be it rubber-energized or spring-energized — allow us to cover gland geometry and extrusion gaps, which are again highly dependent on the temperature range we’re trying to span.
With large temperature swings, we need to allow the seals to follow a non-standard bore material, like Nylon, which could grow to the point that our seals won’t follow.
Using rubber or metallic springs allows us to compensate for a wide range of changing diameter due to changes in temperature.
When temperatures exceed 750°F, we consider the use of carbon seals energized by steel bands to handle temperatures over 1200°F.
While our goal may not be to make a perfect seal, the rigors of working at these elevated temperatures causes the seal designer to help establish what the hardware will ultimately look like.
Sealing using materials around their glass transition temperatures requires care to ensure the seal will return to a state usable for future temperature excursions.
Similarly, seals used to protect against leakage during a fire require that the seal fails in such a way as to not leak causing further damage due to the fluid being an accelerant.
One of the fundamental requirements in rotary sealing is for the seal material to stay within a specified PV (Pressure-Velocity) limit.
But our formulas don’t take into consideration temperature, which directly relates to the survivability of a seal. In manufacturing rotary seals, there is a strong need to reject heat and continue to seal as the material softens due to the increased temperatures.
Similarly, some materials are not suited for temperature excursions in rotary service such as UHMW , however UHMW does an excellent job in sealing water. So if the temperature continues to be low, or stays low due to the product flowing through the system, UHMW might be the best material.
While many applications may be well-suited for a simple O-ring , when factors like temperature come into play, this causes the designer to consider the impact of the environment.
In combination with pressure and fluids, temperature could be the major factor in the design of a seal. And one of the industries that relies heavily on seals that can withstand extreme temperatures is the aerospace industry.