Eclipse goes to Mars

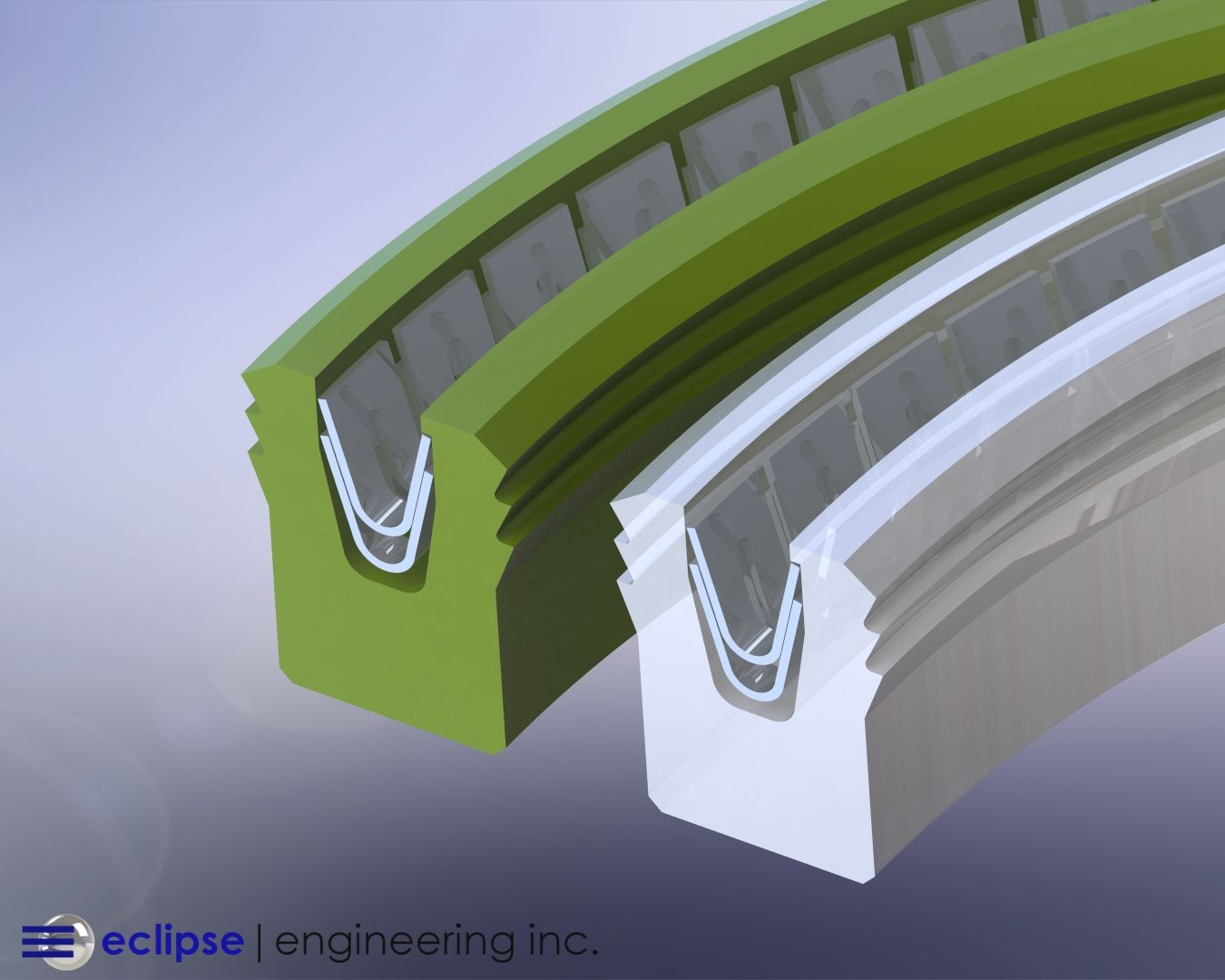
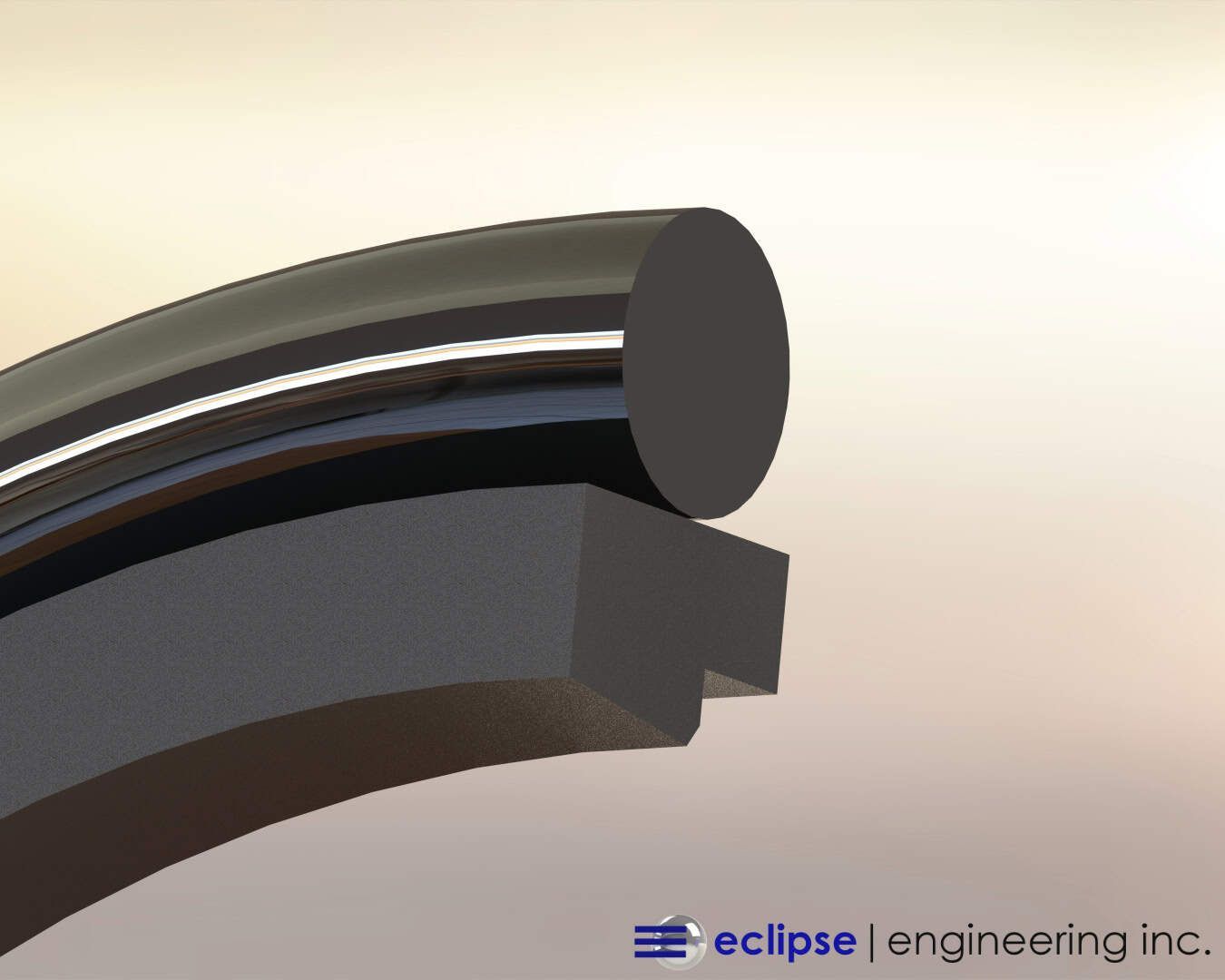
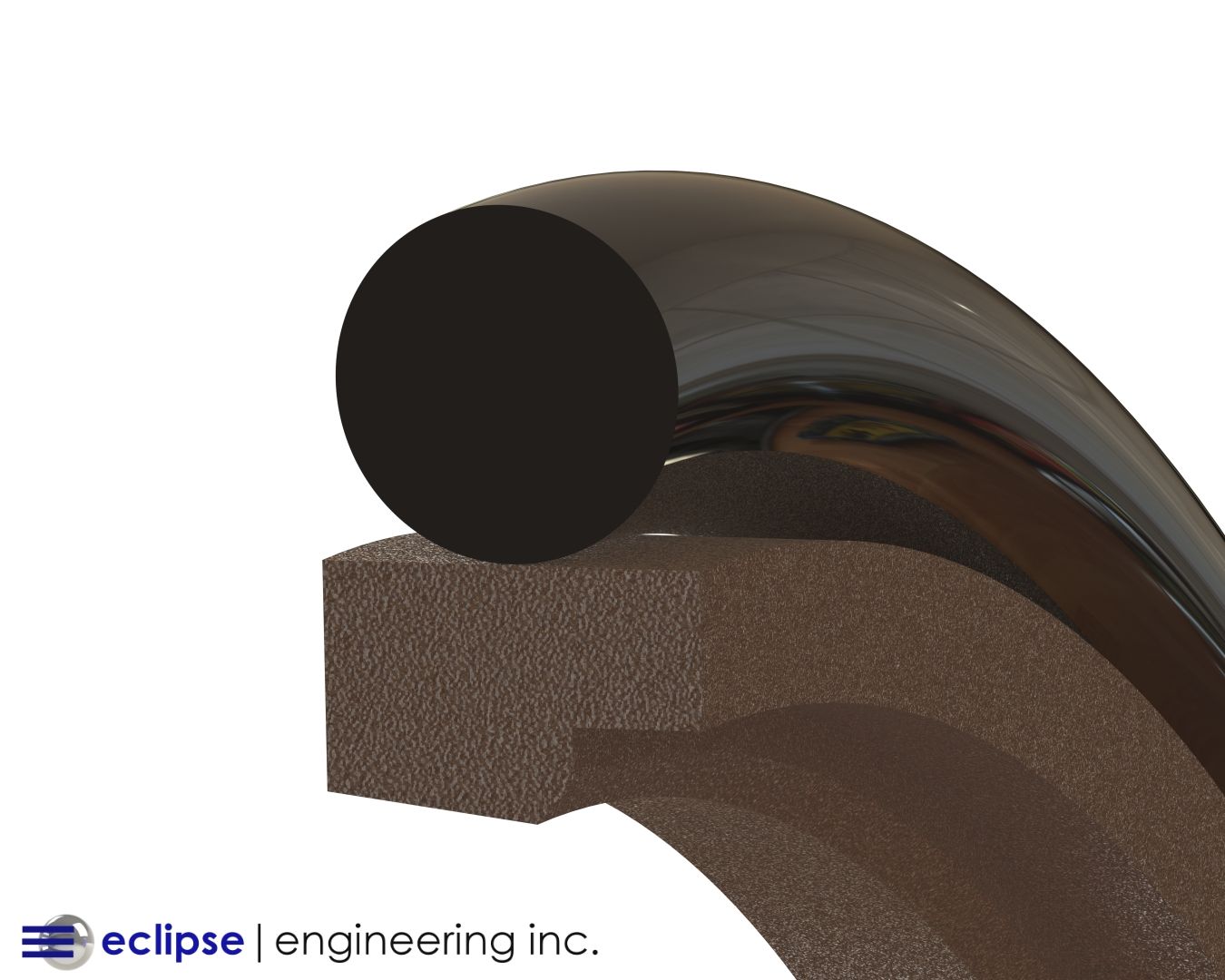
When Spirit and Opportunity descended to the Martian surface, seals from Eclipse Engineering were on board. One set of seals protects the asmith drive assembly from the very fine dust particulate found on the Martian surface. These seals allow the camera mast to rotate 360 degrees.
A second set of seals is located on the pivot point just below the camera to allow the camera to pivot up and down on the horizon. These seals also protect the drive mechanism from the Martian dust.
In the image above, one set of seals is located below a hexagonal box which contains the asmith drive assembly. The second set is located just below the twin camera mount.