Seal Contaminants: What They Are and How to Prevent Them

Neglecting routine maintenance can cost you in seal performance or, in some cases, end with catastrophic failure. Prolonged downtime will incur losses that exceed the temporary cost of preventative maintenance.
It’s important to identify seal contaminants and their sources before they turn into larger issues. Here are some tips on what to look for and how to deal with them.
Common contaminants
- Here are some typical contaminants you’ll come across:
- From original manufacture: debris, casting sand, paint, pipe sealant, cleaning rag fibers and weld spatters
- Pre-existing particle matter in system fluid before being entered into the system (through lack of pre-filtering)
- Ingressed contamination through rod/piston seals, component seals or poorly fitted covers, such as dirt, mud, water, dust and oil
- Ingressed particles that attract or generate larger particles causing abrasion, corrosion, cavitation, erosion and fatigue from the chafing between moving parts
- Catalytic contamination from water, air or heat causing chemical reaction with other particles in a fluid
Inspections: what to look for
Some of the above contaminations are easier to detect than others.
For cylinders and actuators, take note of scoring, putting or accumulated hydraulic fluid on pistons/rods, which could indicate that metal particles have got into the system. If so, the system’s oil needs to be drained, and the entire system flushed out. Seals need to be inspected for damage and wear and thoroughly cleaned or replaced.
Consider any strong or unusual smells, which may indicate your system is operating at excessive temperature, fluids are leaking onto high-temperature surfaces, or fluid viscosity has been compromised.
Remember that if fluids can get out through seals, contaminants can get in. A hydraulic fluid leak could indicate serious damage to your system and spell major cost to your business.
You can’t usually see contaminants within fluids with the naked eye, so fluid sampling and chemical lab analysis is required. Particle count is a good measure of contamination and its damage potential.
Putting it right
Once you know which contaminants are present, you can find out their source and how to eradicate or minimize them.
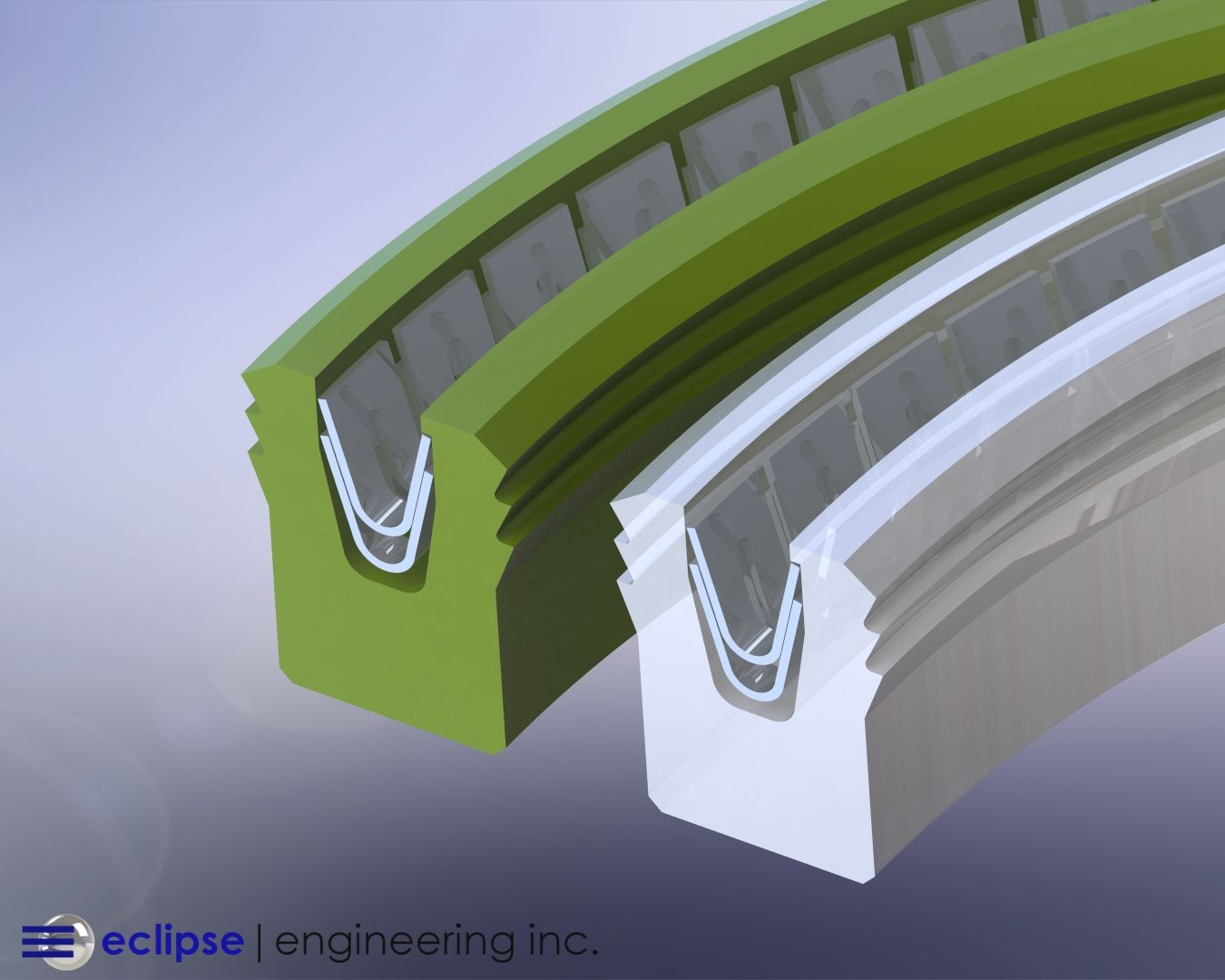
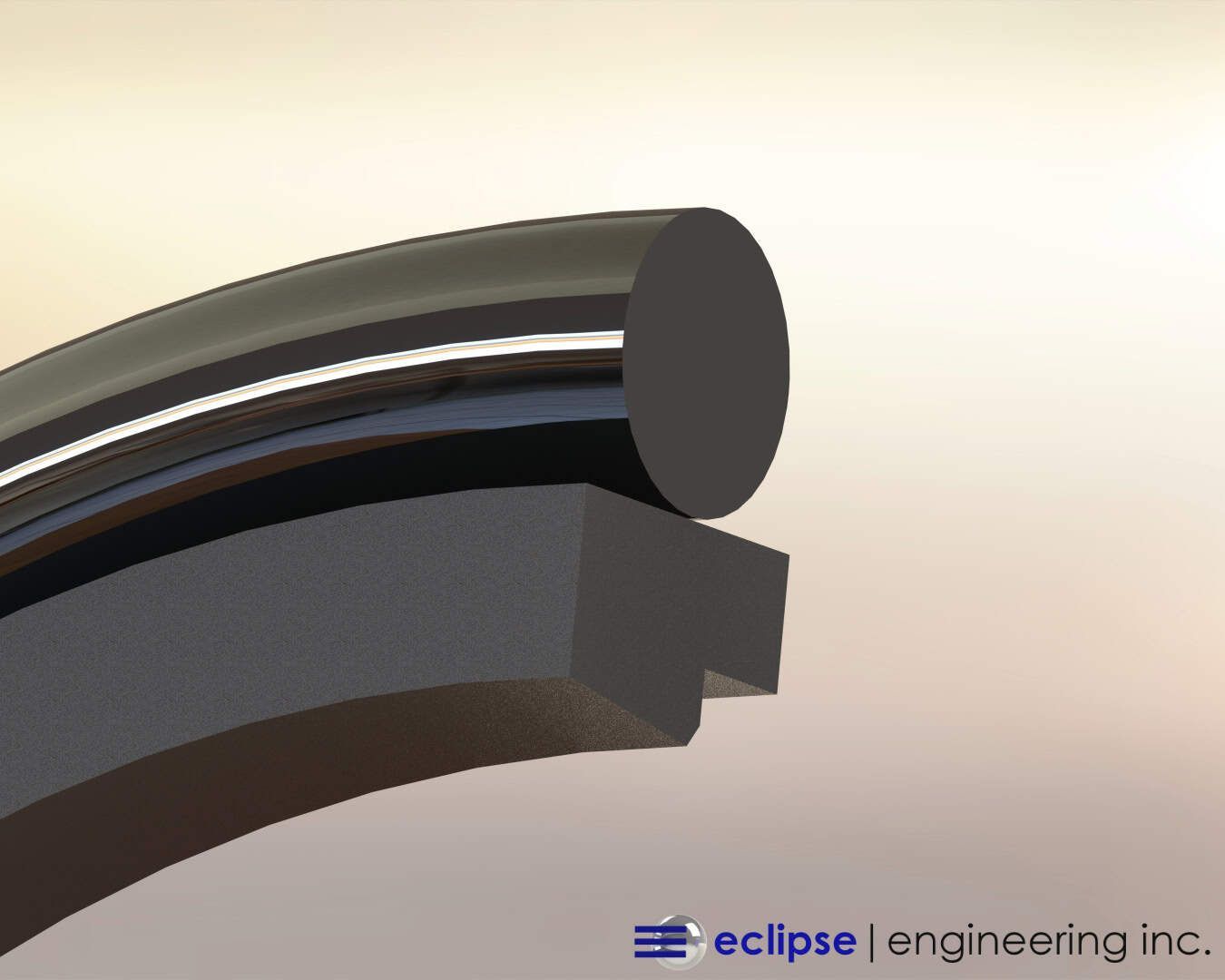
Even without contaminants present, it’s crucial to check the condition of your seals and replace them if necessary with better suited ones.